深度学习课程需要做一个project,我们组选了Lottery Ticket Hypothesis这个课题,最近做了一些调研,简要的记录在此。
Background
“The Lottery Ticket Hypothesis: Finding Sparse, Trainable Neural Networks” 是ICLR 2019年的best paper,主要贡献是提出了一种模型剪枝的启发式算法。
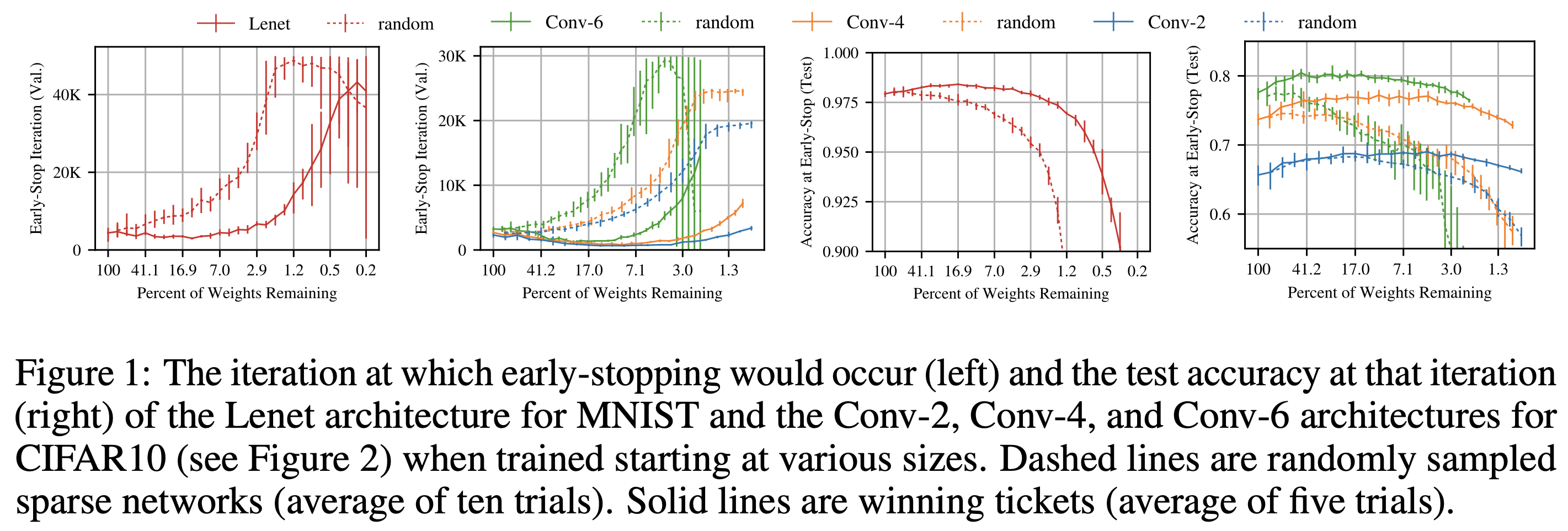
虽然深度学习网络中往往存在大量冗余的参数,但是被剪枝过的网络通常很难训练,并且最后的准确率也会有所下降。在上图中,每种颜色代表一种网络结构,虚线是被传统方法剪枝后的稀疏网络,虚线是用本文方法剪枝后的网络。对比左边两幅图,可以看出随着不断的剪枝,训练需要的迭代次数会大幅度增加。再对比右边的两幅图,可以看到,随着剪枝,准确率是在不断下降的。
Lottery Ticket Hypothethsis
因此作者提出彩票假设,认为一个随机初始化的神经网络,存在一个子网络。这个子网络可以独立的训练,迭代次数比原来网络少,准确率比原来网络高。
A randomly-initialized, dense neural network contains a subnet- work that is initialized such that—when trained in isolation—it can match the test accuracy of the original network after training for at most the same number of iterations.
用数学语言表示就是:

其中$m$和$\theta_0$是对应的,$\theta_0$不同,找到的$m$也不一样。作者把这个叫做winning ticket。
Identifying Winning Tickets

Pruning Methods
剪枝策略可以按不同的角度分类:
When to prune?
- Before / During / After training
How often?
- One-shot / Iterative
How to prune?
- Magnitude / Gradient-based / Learned
What to prune?
- Structure / Unstructure
- Local / Global
红色表示本文方法所在类别。
需要注意的是,LTH找到的winning ticket只是训练前的网络结构,还需要进一步训练。
LTH用的是Iterative剪枝方法,也就是需要迭代的剪枝,而不是剪一次就结束。
通过阅读源码,我们可以看到,具体到每一个epoch,作者对于所有参数,从小到大选择其中p%,然后将其mask置为0。
作者在appendix中对比了Structure和Unstructure两种方法,以CNN为例,结构化剪枝指的是一整个kernel要么保留、要么全部剪掉;而非结构化方法指的是可以将kernel中某些参数剪掉。结构化方法的优势在于真正大幅度降低了计算量,非结构化方法虽然剪掉了许多参数,但网络参数非常稀疏,硬件资源无法针对这种网络进行计算上的优化。而结构化方法的优势在于相比于非结构化方法,其performance往往要好很多。
最后local和global指的是,剪枝时整个网络的参数一起比大小然后剪枝,还是每层分别比大小剪枝,前者是global,后者是local。
Experiments
数据集为MNIST、CIFAR-10、CIFAR-100,base model为MLP、LeNet、ResNet-18、VGG-19等。相比于随机剪枝,用LTH方法剪枝可以在几乎和原网络相同的迭代次数下,达到原网络的效果。
另外作者发现dropout在剪枝后的模型上依然适用,可以达到正则化的效果。
调研方向
Stabilizing the lottery ticket hypothesis
Summary: Instead of reset back to initial values $\theta_0$, rewind to $\theta_k$ after training iteration $k$.
Can research:
- To which point we rewind to?
- Find a strategy for rewinding: ex. Find a metric for rewinding and justify the metric intuitively (theoretically if we can)
Pruning is all you need
Summary: Instead of resetting and training, just prune the network and there exists a winning ticket.
Can research:
- How to find a winning ticket (provide an algorithm).
- How performance can change when size is not as large? (dataset size)
- (Theoretical) What’s the condition that it exits? Or show that it’s hard to find such a winning ticket.
- Effects of width and depth.
We already know a very wide network is sufficient for finding a winning ticket. Show or disprove the conjecture: a deep but not wide network may not have a winning ticket. - Assume that a winning ticket exists, is there a theoretical proof that it’s better? (this question is not well-formulated)
- To what extent do we prune?
- For each of the above, can discuss differences between say MLP or CNN. (In terms of pruning techniques, results etc.)
Pruning and compression
对这个领域没有了解,不打算做