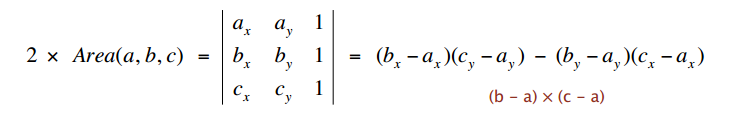1 凸包(Convex hull)
凸包:假设平面上有 n 个点,过某些点作一个多边形,使这个多边形能把所有点都“包”起来。当这个多边形是凸多边形的时候,我们就叫它“凸包”
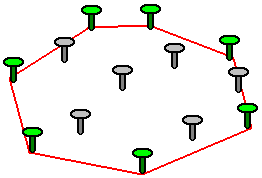
凸包问题:给出点的数目和各个点的坐标,求构成凸包的点
2 凸包应用(Convex hull application)
2.1 应用 1:运动规划(motion planning)
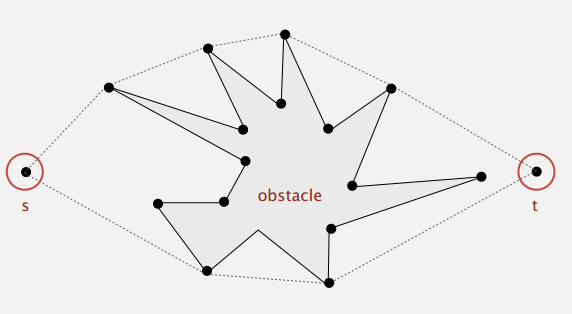
机器人运动规划:寻找可以从点 s 到点 t 的能够避开多边形障碍物的最短路径
最短路径是 s 到 t 的直线或者是凸包的两条路线之一
2.2 应用 2:最远配对(farthest pair)
最远配对问题:给出平面上的 N 个点,从中选出欧氏距离最大的一对点
最远的点一定是凸包的顶点
3 Graham 扫描法
选取纵坐标最小的点作为起点,如图 4 中的 P0
按照以 p0 为起点的极角从小到大的顺序,将其它所有的点进行排序
依次考虑每个点:如果可以产生一个逆时针旋转(counterclockwise turn),就留下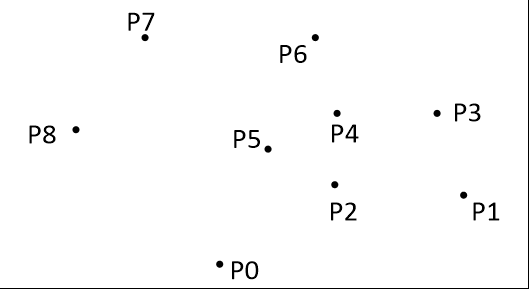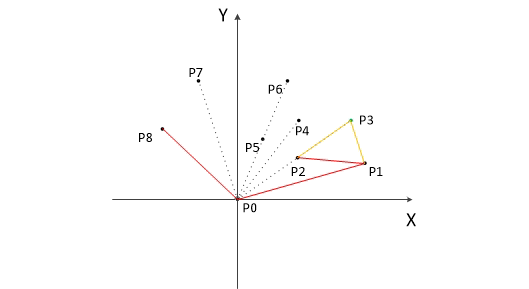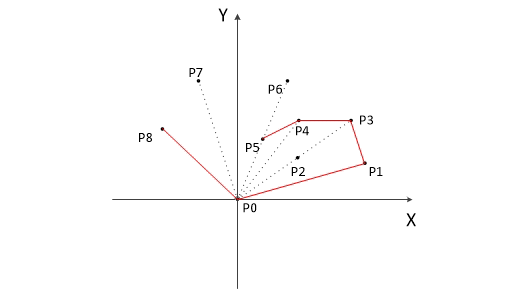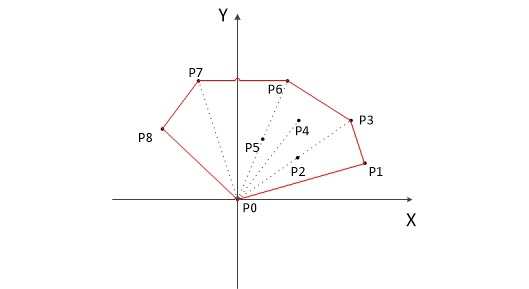
3.1 判断逆时针旋转(Implementing ccw)
给出 3 个点 a,b,c,判断 a->b->c 是否是逆时针旋转
分别算出直线 ab 和 cd 的斜率,通过比较两个斜率决定是否为逆时针旋转
具体算法如下:
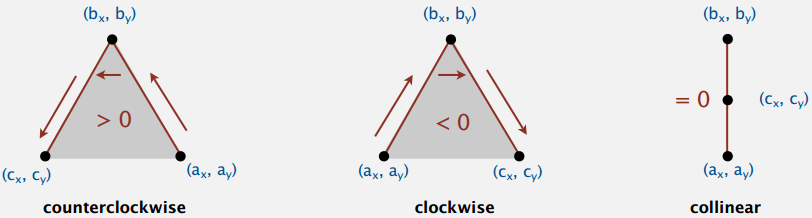
CCW. Given three points a, b, and c, is a → b → c a counterclockwise turn?
- Determinant (or cross product) gives 2x signed area of planar triangle.
- If signed area > 0, then a → b → c is counterclockwise.
- If signed area < 0, then a → b → c is clockwise.
- If signed area = 0, then a → b → c are collinear.
3.2 代码
3.2.1 判断逆时针旋转
1 | public class Point2D |
3.2.2 排序
简化假设:不存在三点共线;至少有 3 个点
1 | Stack<Point2D> hull = new Stack<Point>(); |
运行时间:排序:NlogN;剩余部分:线性
每个点出入栈最多一次